A CT scan is a complex X-ray usually timed with the ECG to produce 3D images of the chest including the heart and the aorta. It uses radiation ( modern machines use relatively little)to focus on the heart area and gather data very quickly- in one beat of the heart. If information about the […]
This is done if there is any suggestion of an abnormal rhythm or heart block occurring intermittently. This might be because of an abnormality on the resting ECG (e.g. extra beats or a minor degree of heart block) or a symptom like a dizzy spell or blackout or severe palpitation (a sense of an abnormal […]
The normal echocardiogram is performed with the patient at rest even though symptoms related to heart valve disease occur on exertion. In some people a stress echocardiogram which mimics exertion is needed for a complete examination. This can be requested for a number of reasons: Reasons to perform a stress echocardiogram in heart valve disease: […]
For the test you will lie on your left side and local anaesthetic is sprayed into the mouth before a tube is inserted through the mouth. You will be asked to swallow to help the tube into the gullet (oesophagus). Intravenous sedation is usually offered to patients. The tube, or scope, is similar to those […]
Normally you will be told to take no food or fluids (nil by mouth) for at least 6 hours before your procedure but the times may vary between different hospitals. You should receive a letter from your hospital with a full explanation and a list of possible cautions or contraindications. These could include, enlarged veins […]
A transoesophageal echocardiogram is not needed routinely but may be necessary to produce more detailed images than conventional echocardiography: The procedure is performed usually as a day-case and usually under sedation. Many patients naturally feel very anxious prior to this procedure. Sedation usually means that the procedure is very well tolerated and often patients […]
This is a gentler test. You will be asked to walk laps up and down a corridor of a predetermined distance for 6 minutes. You can stop whenever you need to rest and restart when you feel able. The distance you walk in 6 minutes is recorded. This can be a useful test for demonstrating […]
Stickers are placed on the chest to record the electrical activity of the heart. You are then asked to walk on a treadmill whilst your blood pressure and heart rate are monitored. This is recommended in many patients with severe valve disease and normally functioning left ventricles who genuinely have no symptoms – even after […]
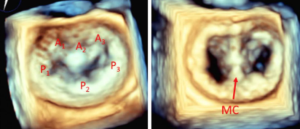
This is an ultrasound scan of the heart and it is harmless. Echocardiograms are usually done in hospital, sometimes in community centres. A full study usually takes 30-45 minutes. During the test an ultrasound probe is placed on the chest and moving pictures of the heart are taken. The echocardiogram not only diagnoses valve disease, […]
Stickers are placed on the chest and the electrical activity of the heart is recorded. A resting ECG is routine for a new patient, although it does not usually show specific abnormalities associated with valve disease. It may also be requested after any change in symptoms including an event like a dizzy spell, or if […]