What is the pulmonary valve? The pulmonary valve is the main outlet valve on the right side of the heart. It allows blue (deoxygenated) blood to leave the heart after the right ventricle has contracted. Once the blood has left the heart the pulmonary valve closes and stops any blood falling back into the right […]
What is the tricuspid valve? The tricuspid valve is the inlet valve on the right circuit. It opens to let blood flow from the right atrium to right ventricle, then closes to stop blood flowing backwards. The tricuspid valve consists of three leaflets. This valve is thinner and more delicate than the mitral valve and […]
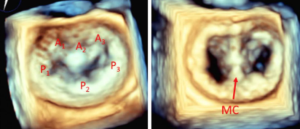
What is the mitral valve? The mitral valve is a valve with two leaflets situated on the left side of the heart. It is a one-way valve that allows blood to move from the top chamber of the heart (left atrium) to the bottom chamber (the main pump – the left ventricle). What is mitral […]
What is the mitral valve? The mitral valve is a valve with two leaflets situated on the left-hand side of the heart. It is a one-way valve that allows blood to move from the top chamber of the heart (left atrium) to the bottom chamber (the main pump – the left ventricle). What is mitral […]
What is the mitral valve? The mitral valve is situated on the left side of the heart. It is a one-way valve that allows blood to move from the top chamber of the heart (left atrium) to the bottom chamber (the main pump – the left ventricle). What is mitral regurgitation? Mitral regurgitation is a […]
What is the aortic valve? The aortic valve is a structure in the heart that allows one way flow of blood out of the main pumping chamber of the heart (the left ventricle) into the main blood vessel leaving the heart (the aorta). When the heart muscle pumps, the aortic valve opens allowing blood to […]
What is the aortic valve? The aortic valve is the main outlet valve of the heart which allows blood to exit with every heartbeat. It is a one-way valve that closes after the blood has left the heart. It is attached to the main blood vessel that exits the heart, the aorta. What is […]
What is the aortic valve? The aortic valve is the main outlet valve of the heart and allows blood to exit with every heartbeat. Normal aortic valves have three leaflets, but around 1 in 50 people are born with an abnormal heart valve which has two leaflets, known as a bicuspid aortic valve. What is […]
Video 1 What is cardiac catheterisation? This is a procedure to investigate the coronary arteries. The coronary arteries are vessels which leave the main blood vessel (aorta) and run along the surface of the heart supplying the heart muscle with blood. They can become lined/furred with cholesterol plaque (atherosclerosis) over time. Most patients who are […]
This test uses a strong magnet to modify the atoms in the body for a tiny instant of time. It does not use radiation and there are no known side-effects other than very rare kidney effects if a ‘dye’ called gadolinium is used if the kidney function is already significantly compromised. It is used in […]